Definition and Purpose
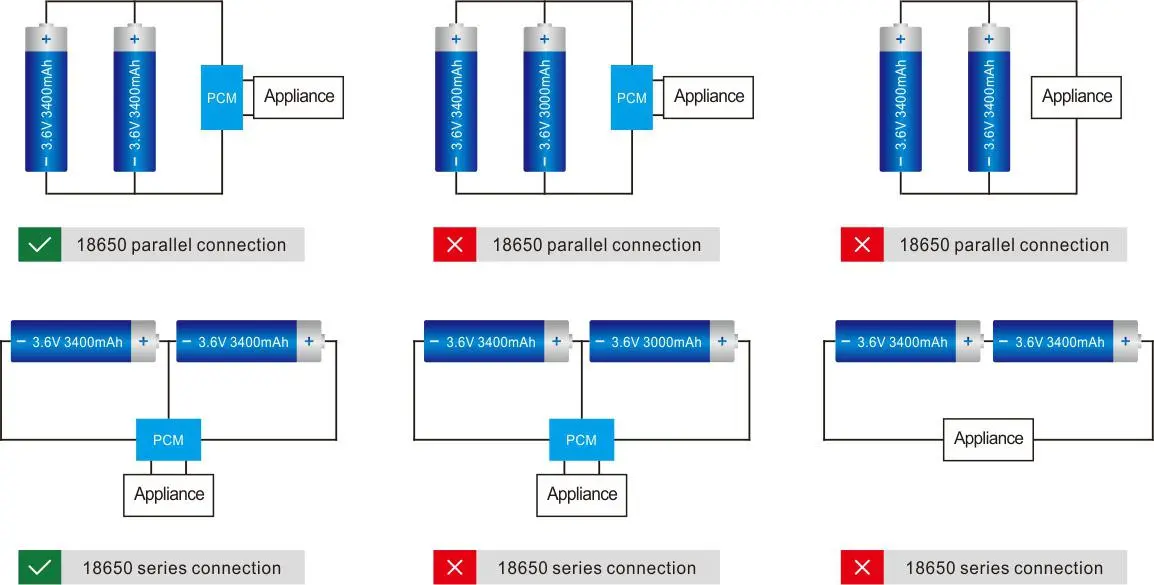
Series connection involves connecting multiple LiFePO4 batteries in a sequence, end-to-end, to achieve a higher overall voltage. By connecting batteries in series, the individual voltages add up, resulting in a combined voltage that meets specific requirements for a particular application. Series connection is commonly employed when the voltage demand exceeds the capacity of a single LiFePO4 battery.
How Series Connection Works
In a series connection, the positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next battery, and so on until the desired number of batteries is connected. The total voltage across the series-connected batteries is the sum of the individual battery voltages. For instance, if each LiFePO4 battery has a voltage of 3.2 volts and four batteries are connected in series, the total voltage across the series would be 12.8 volts.
Benefits of Series Connection
Series connection of LiFePO4 batteries offers several advantages:
- Higher Voltage: Series connection allows for the creation of higher voltage battery banks, enabling the power supply to meet the requirements of specific applications.
- Increased Energy Storage: Connecting batteries in series increases the overall energy storage capacity, which is vital for applications demanding extended periods of power supply.
- Simplified Wiring: Series connection simplifies the wiring configuration as batteries are connected sequentially, reducing the complexity and minimizing the number of interconnections.
- Balancing and Monitoring: Series-connected batteries require monitoring and balancing systems to ensure proper voltage distribution and prevent overcharging or discharging of individual cells.
- Flexibility: Series connection provides flexibility in designing battery systems to meet voltage requirements, allowing customization for various applications.
Factors to Consider for Series Connection
Successful series connection of LiFePO4 batteries requires careful consideration of various factors:
Battery Capacity
When connecting batteries in series, it is essential to ensure that they have the same capacity. Mismatched capacities can lead to imbalanced charging and discharging, reducing the overall performance and lifespan of the battery bank.
Battery Voltage
LiFePO4 batteries have a nominal voltage of around 3.2 volts per cell. Before series connecting batteries, it is crucial to verify the voltage rating and ensure compatibility. Mixing batteries with different voltage ratings can lead to imbalances, affecting the overall performance and safety of the battery bank.
Balancing and Monitoring
Series-connected batteries require a balancing and monitoring system to maintain uniform voltage levels across all cells. Balancing circuits help equalize the charge levels of individual batteries, preventing overcharging or over-discharging. Monitoring systems provide real-time data on the voltage of each cell, allowing users to identify any imbalances or issues promptly.
Wiring and Connections
Proper wiring and connection techniques are critical for the safety and efficiency of a series-connected LiFePO4 battery bank. High-quality cables, appropriate fusing, and secure connections should be utilized to minimize resistance, voltage drops, and potential hazards.
Steps for Series Connection
To successfully connect LiFePO4 batteries in series, follow these steps:
Precautions and Safety Measures
Before proceeding with the series connection, ensure that you follow safety guidelines and take necessary precautions, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and working in a well-ventilated area.
Ensuring Battery Compatibility
Verify that the LiFePO4 batteries you plan to connect in series have the same voltage rating and capacity. Mixing different battery brands or models may result in imbalances and reduce overall performance.
Proper Wiring and Connection Techniques
Use high-quality cables, connectors, and wiring methods to establish secure and low-resistance connections. Properly insulate and protect the connections to minimize the risk of short circuits or electrical hazards.
Testing and Verification
After making the series connections, test the voltage across the battery bank to ensure it matches the desired voltage. Additionally, monitor the individual battery voltages to ensure balanced charging and discharging.